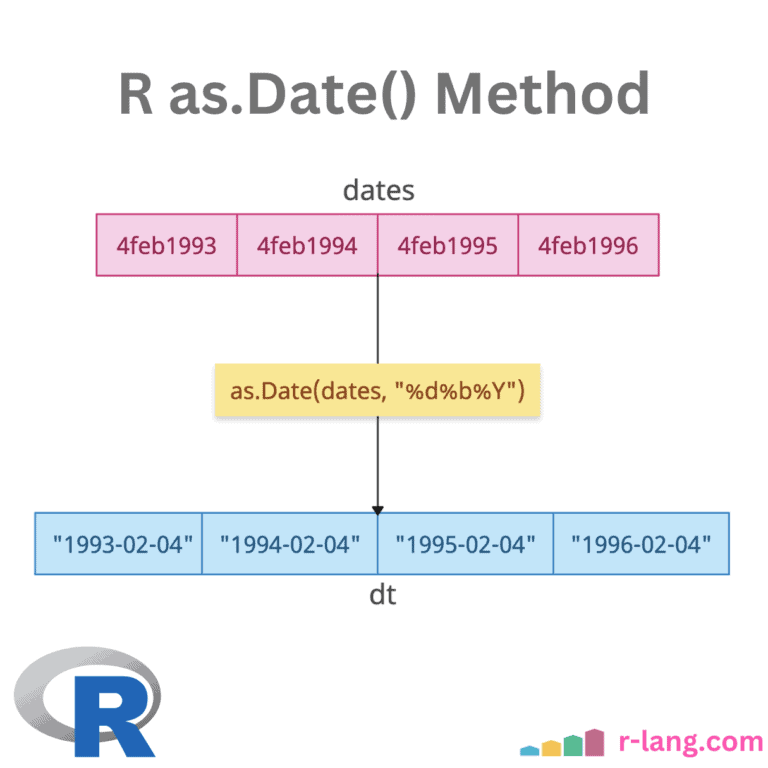
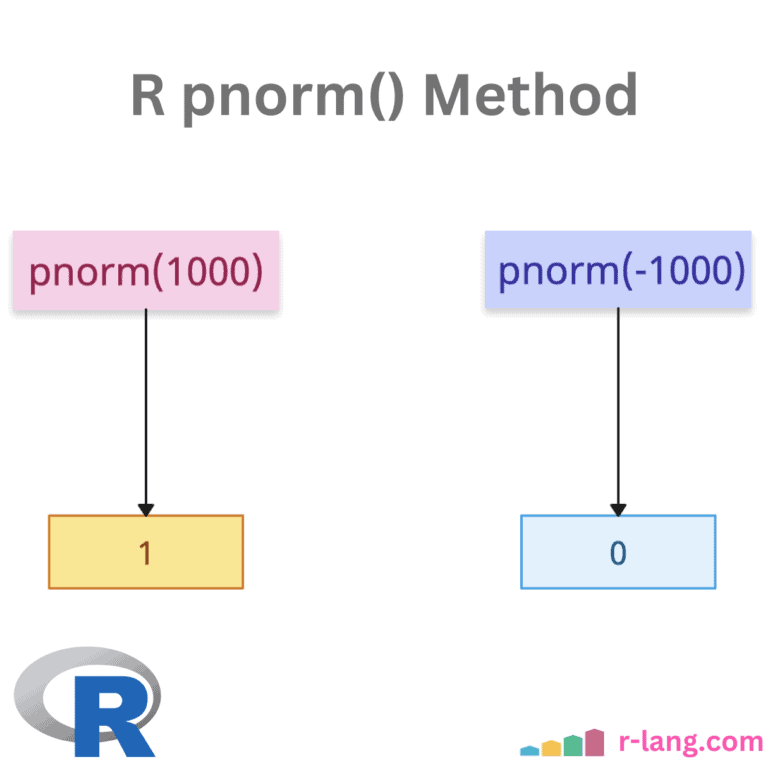
summary() Function: Producing Summary Statistics in R
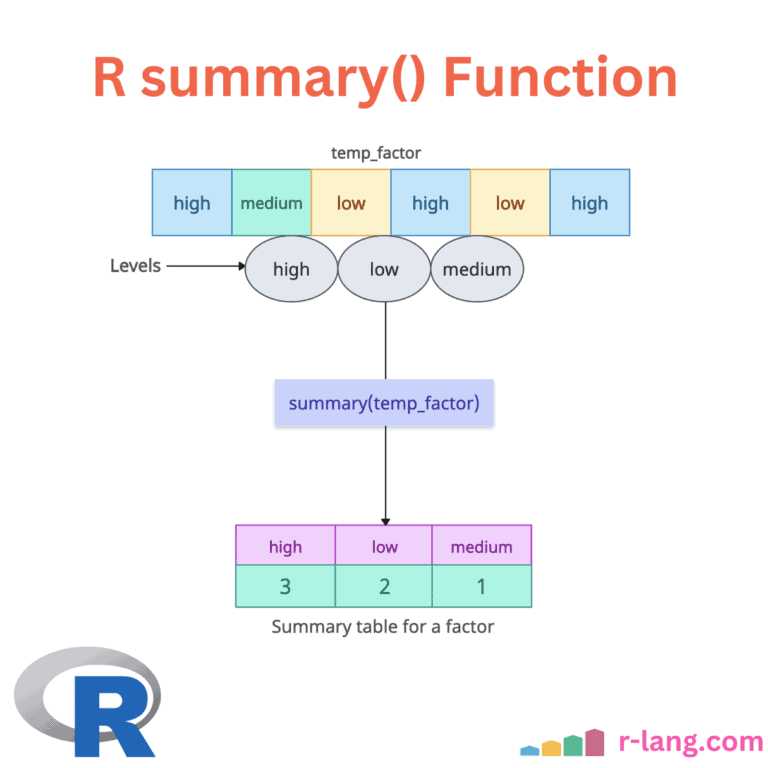
The summary() is a generic function that produces the summary statistics for various R objects, including vectors, matrices, data frames, and model objects. The above figure explains the summary for a data frame with three columns. For different types of objects, the summary() function produces different types of summaries: If the input is numeric, it … Read more