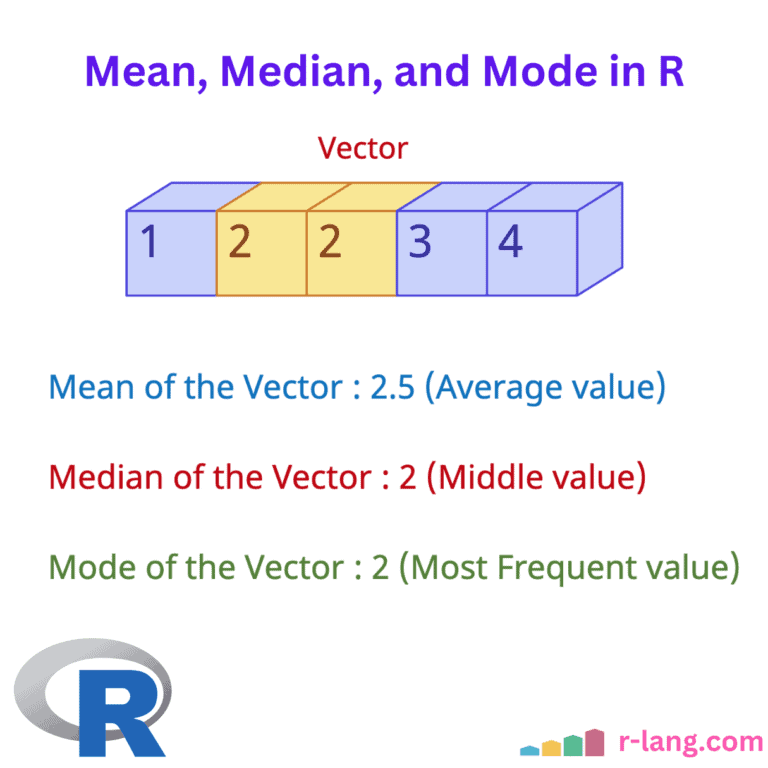
NOT IN (%!in%) Operator in R
The %in% operator checks whether the element is present. And NOT IN (%!in%) operator does the exact opposite. The %!in% is a custom operator that checks if the elements of one vector are not present in another vector. It returns a logical vector of the same length as the left-hand vector, with TRUE for those … Read more