R dplyr::summarise() or summarize() Function
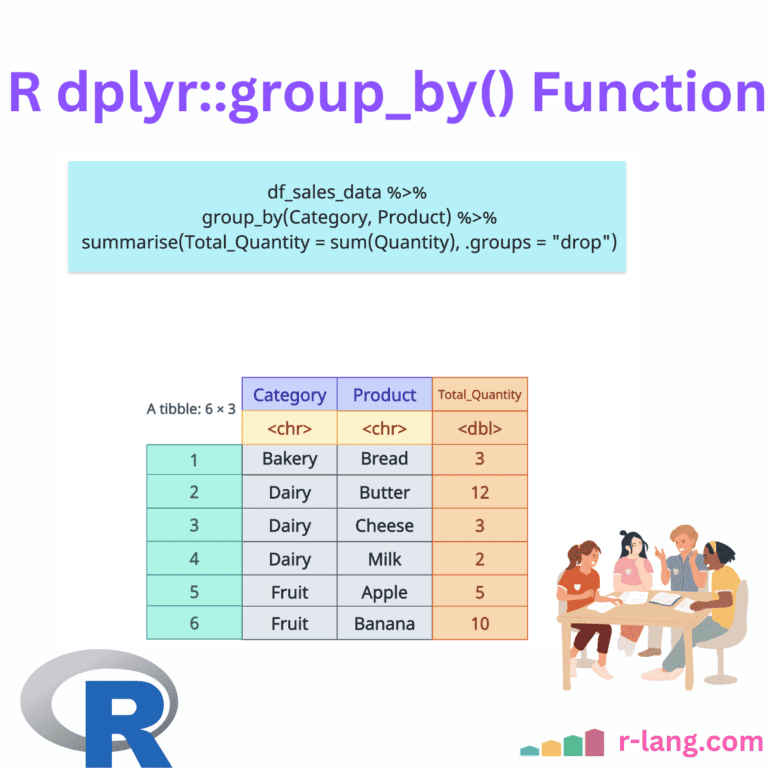
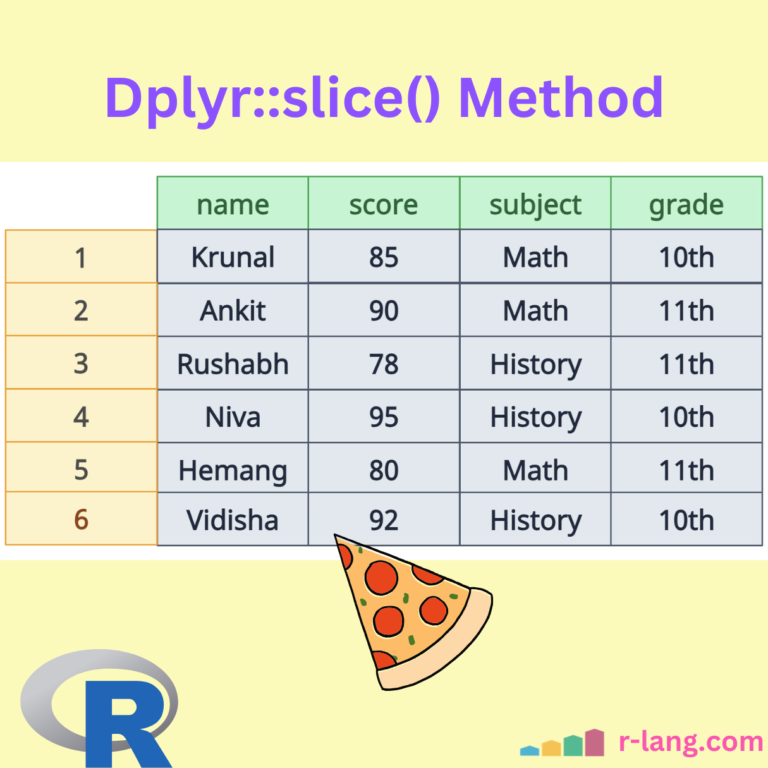
The dplyr summarise()(or summarize()) function aggregates data into a single summary value for each group or the entire dataset if ungrouped. It collapses multiple rows into a concise statistical summary, such as the mean, sum, and count. Developers often use summarize() with group_by(), which splits the data into groups based on one or more categorical variables (Columns … Read more