The standard deviation is a measure that tells you how spread out data are in a dataset. It is a measurement of the dispersion of the values.
Picture this: You and your friends live near each other and daily walk to the school. If you count the total number of steps you and your friend take, it will be roughly the same, and the standard deviation will be low because you both live near each other. If there is a huge difference between you and your friend’s steps, then that means the standard deviation is high.
If the standard deviation is higher, then the spread of values is wider.
If the standard deviation is lower, then the spread of values is narrower.
It shows the central tendency, which is helpful in any type of data analysis.
To calculate the standard deviation in R language, use the “sd()” function.
Syntax
sd(x, na.rm = FALSE)Parameters
| Name | Description |
| x | It could be a vector of numbers or a column from a data frame. |
| na.rm | It stands for NA remove.
If FALSE, NA values will be included in the calculation. If TRUE, NA values won’t be included in the calculation. |
Return value
The sd() function returns a numeric value representing the standard deviation.
Example 1: Finding the standard deviation of a numeric vector
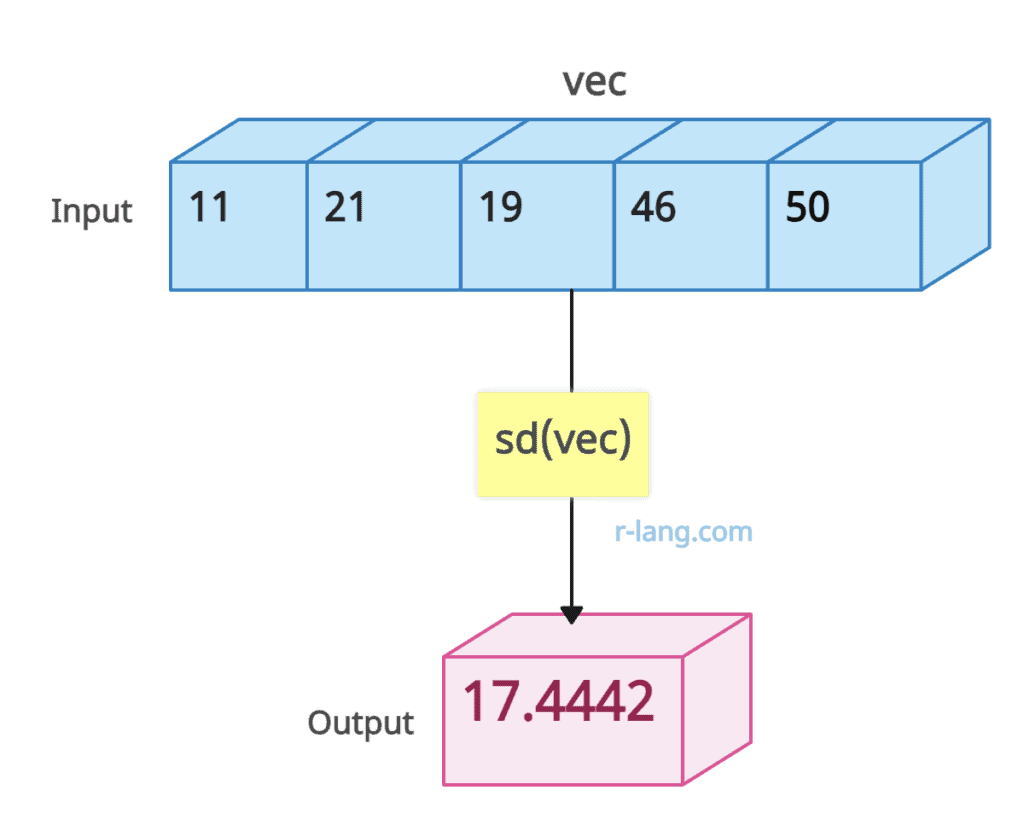
# Create a numeric vector using c() function
vec <- c(11, 21, 19, 46, 50)
# Find the standard deviation of the vector using sd() function
stddev <- sd(vec)
# Print the standard deviation using the print() function
print(stddev)Output
[1] 17.4442Example 2: Using Array

rv <- c(19, 21)
rv2 <- c(46, 4)
arr <- array(c(rv, rv2), dim = c(2, 2, 2))
cat("The standard deviation of array is", "\n")
sd(arr)Output
The standard deviation of array is
[1] 16.11565Example 3: Using Matrix
In the above figure, we are finding the sd of the whole matrix.
mat <- matrix(1:9, ncol = 3)
sd(mat)
Output
[1] 2.738613
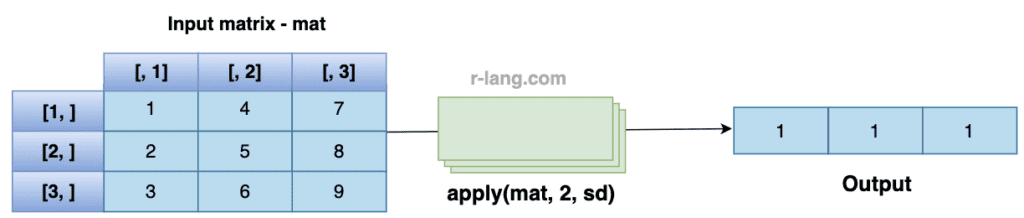
To calculate the standard deviation of each column, you need to use the “apply()” function in combination with the sd() function.
In the above figure, we calculated the standard deviation of each matrix column.
mat <- matrix(1:9, ncol = 3)
apply(mat, 2, sd)Output
[1] 1 1 1
Example 4: Handling NA values
Pass the na.rm = TRUE argument within the sd() function to handle NA values in the data frame. This argument tells R to remove NA values before performing the calculation.
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(1, NA, 3),
col2 = c(NA, 5, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, NA)
)
sds <- apply(df, 2, sd, na.rm = TRUE)
sds
Output
col1 col2 col3
1.4142136 0.7071068 0.7071068
Example 5: Using Real Dataset with Visualization
Use the read_csv() method to import the real-world dataset in R.
For this tutorial, we will use Kaggle’s StudentPerformance.csv file as a dataset and find the standard deviation of the “math score” column.
Step 1: Install the required libraries
You need to install tidyverse and ggplot2 libraries if you have not already!
install.packages("tidyverse")
install.packages("ggplot2")Step 2: Load the dataset
library(tidyverse)
library(ggplot2)
data <- read_csv("./DataSets/StudentsPerformance.csv")
head(data)Step 3: Finding Standard Deviation
Let’s focus on the “math score” column for understanding standard deviation.
# Using built-in R function for verification
std_dev <- sd(data$`math score`)
print(std_dev)
Output
[1] 15.16308
Step 4: Visualization
We will create a histogram to visualize the distribution of math scores.
On top of this histogram, we will overlay vertical lines to represent the mean and the standard deviations.
# Plot histogram
p <- ggplot(data, aes(x = `math score`))
+ geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..),
binwidth = 5,
fill = "blue", alpha = 0.7
)
+ geom_density(alpha = 0.2, color = "red") + # Adding a density plot
# Add vertical line for mean
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = mean_math),
color = "green", linetype = "dashed", size = 1
) +
# Add vertical lines for standard deviations
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = (mean_math - std_dev_math_builtin)),
color = "purple", linetype = "dotted", size = 0.8
) +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = (mean_math + std_dev_math_builtin)),
color = "purple", linetype = "dotted", size = 0.8
) +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = (mean_math - 2 * std_dev_math_builtin)),
color = "orange", linetype = "dotted", size = 0.8
) +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = (mean_math + 2 * std_dev_math_builtin)),
color = "orange", linetype = "dotted", size = 0.8
) +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = (mean_math - 3 * std_dev_math_builtin)),
color = "yellow", linetype = "dotted", size = 0.8
) +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = (mean_math + 3 * std_dev_math_builtin)),
color = "yellow", linetype = "dotted", size = 0.8
) +
# Add labels and title
labs(
title = "Distribution of Math Scores with Mean & Standard Deviations",
x = "Math Score", y = "Density"
) +
theme_minimal()
# Display the plot
pOutput
The green dashed line represents the mean.
The purple, orange, and yellow dotted lines represent 1, 2, and 3 standard deviations away from the mean, respectively.

Krunal Lathiya is a seasoned Computer Science expert with over eight years in the tech industry. He boasts deep knowledge in Data Science and Machine Learning. Versed in Python, JavaScript, PHP, R, and Golang. Skilled in frameworks like Angular and React and platforms such as Node.js. His expertise spans both front-end and back-end development. His proficiency in the Python language stands as a testament to his versatility and commitment to the craft.