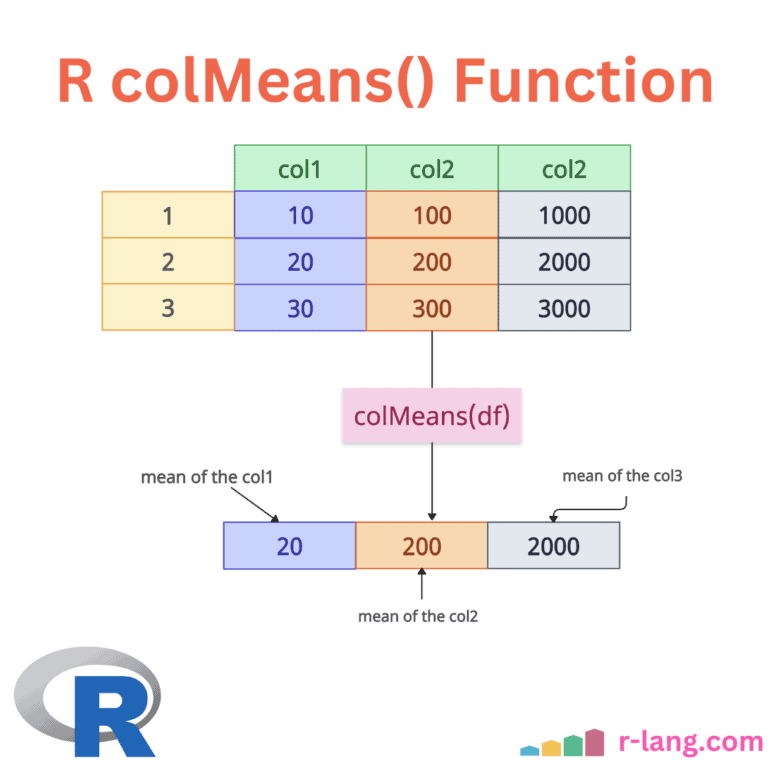
The colMeans() function in R calculates the arithmetic mean of columns in a numeric matrix, data frame, or array. It efficiently calculates the average value for each column by summing the elements and dividing by the number of elements (or non-missing elements if specified).
In the above figure, we defined an input data frame, df, that contains three columns.
The colMeans() function accepts the whole data frame and returns a column-wise mean.
Here is the program that demonstrates the above figure:
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(1, 2, 3),
col2 = c(4, 5, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, 9)
)
# Calculating the mean of every columns.
colMeans(df)
# Output:
# col1 col2 col3
# 2 5 8
Syntax
colMeans(x, na.rm = FALSE)Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| x | It represents an array of two or more dimensions containing numeric, complex, integer, or logical values or a numeric data frame. |
| na.rm | It is a logical argument. If TRUE, NA values are ignored. |
Mean of each column and exclude NA values
What if a data frame contains NA values, and we try to calculate the mean of every column?
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(NA, 2, 3),
col2 = c(4, NA, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, NA)
)
# Calculate the mean of every columns.
colMeans(df)
# Output:
# col1 col2 col3
# NA NA NAWe obtained the output ‘NA’ for every column, as shown in the above figure and code, because ‘NA’ represents a missing value.
To ignore NA values in a data frame, you need to pass na.rm = TRUE.
# Create a data frame.
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(NA, 2, 3),
col2 = c(4, NA, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, NA)
)
# Calculate the mean of every columns.
colMeans(df, na.rm = TRUE)
# Output:
# col1 col2 col3
# 2.5 5.0 7.5
Calculating the mean of specific columns
You can calculate the mean of specific columns based on your requirement by passing the column’s index.
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(1, 2, 3),
col2 = c(4, 5, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, 9)
)
# Calculate the mean col1 and col3
colMeans(df[c("col1", "col3")])
# Output:
# col1 col3
# 2 8For row-wise means, you can use the rowMeans() function.
With a Matrix
A matrix contains rows and columns, and we are only interested in the columns. It works the same as it did with a data frame.
mat <- matrix(1:6,
nrow = 2, ncol = 3,
dimnames = list(NULL, c("A", "B", "C"))
)
colMeans(mat)
# Output:
# A B C
# 3 4 5And it returns the mean of each column.
Matrix with a single element
If the input matrix contains a single element, it returns that element as a mean because there is nothing to compute against. Mean of a single value is that value only.
single_mat <- matrix(5)
colMeans(single_mat)
# Output: 5That’s all!

Krunal Lathiya is a seasoned Computer Science expert with over eight years in the tech industry. He boasts deep knowledge in Data Science and Machine Learning. Versed in Python, JavaScript, PHP, R, and Golang. Skilled in frameworks like Angular and React and platforms such as Node.js. His expertise spans both front-end and back-end development. His proficiency in the Python language stands as a testament to his versatility and commitment to the craft.