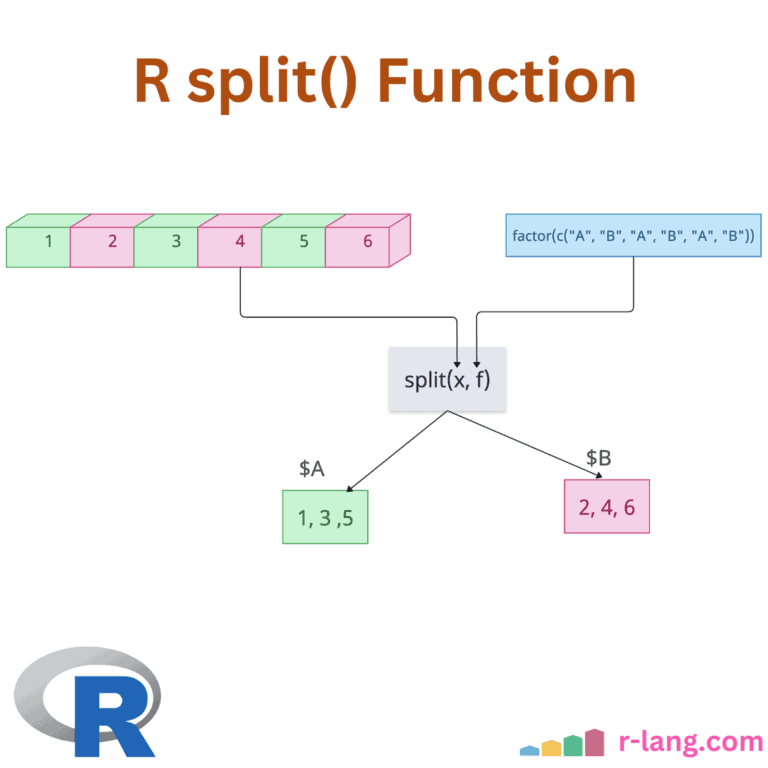
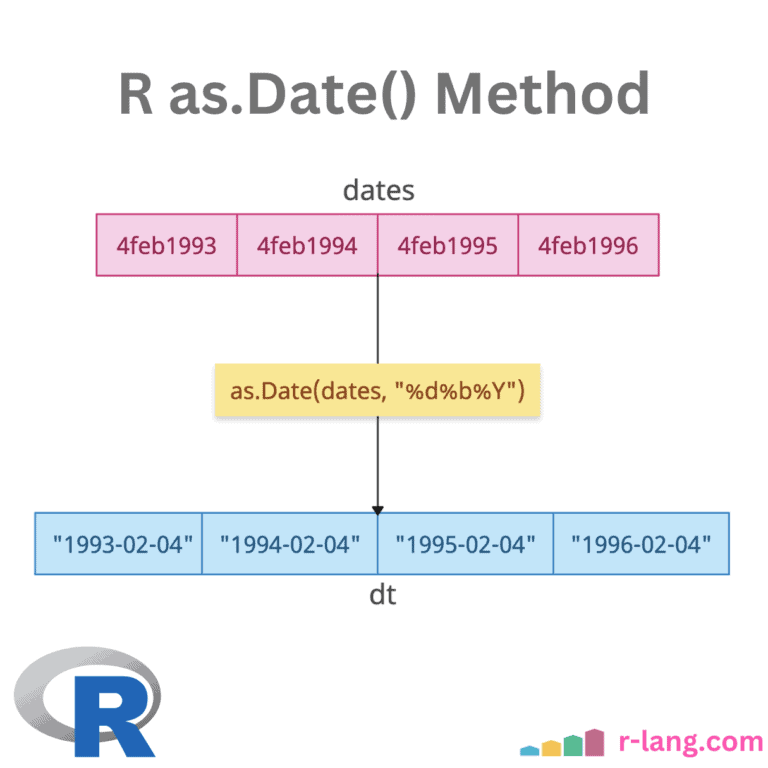
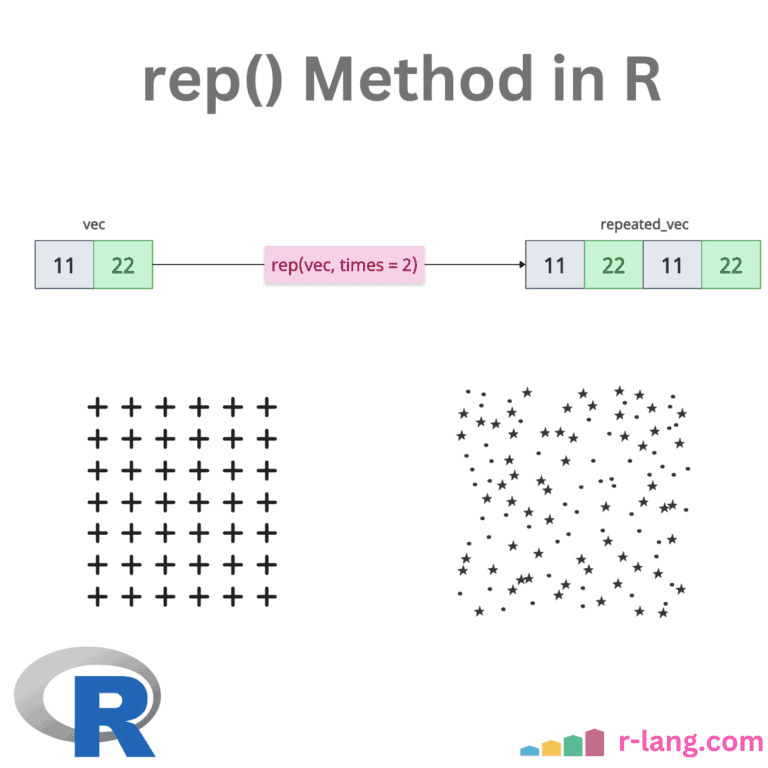
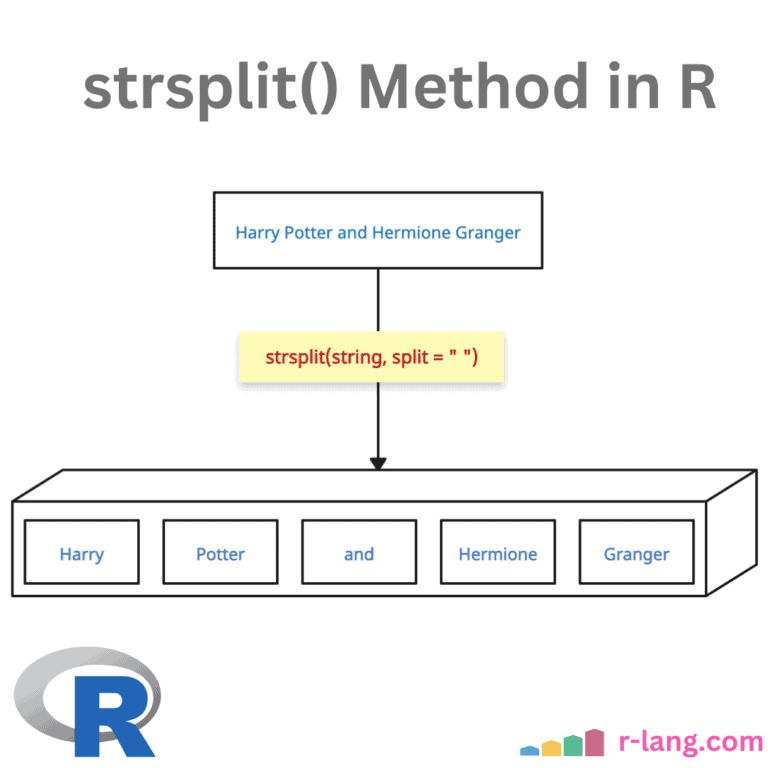
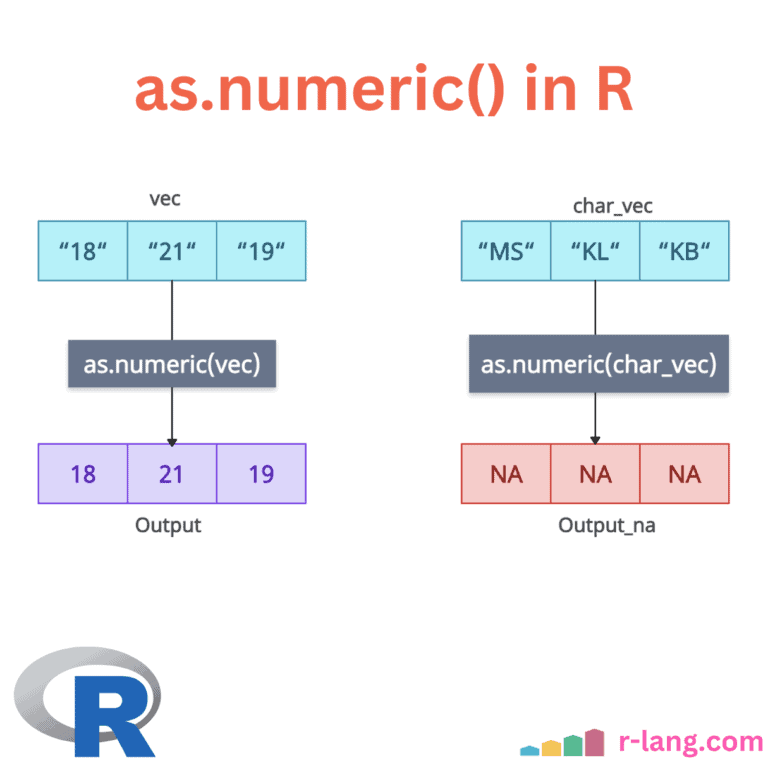
R split() Function: Splitting a Data
The split() function divides the input data into groups based on some criteria, typically specified by one or more grouping factors. The split() function always returns a list, with elements named after the levels of the factor and does not modify the original data. In the above figure, we split the data frame by the … Read more