For understanding the central tendency of your input dataset, you need to calculate the basic summaries like mean, median, and mode. It gives you the data distribution, which tells you whether it is symmetrical or skewed.
Mean
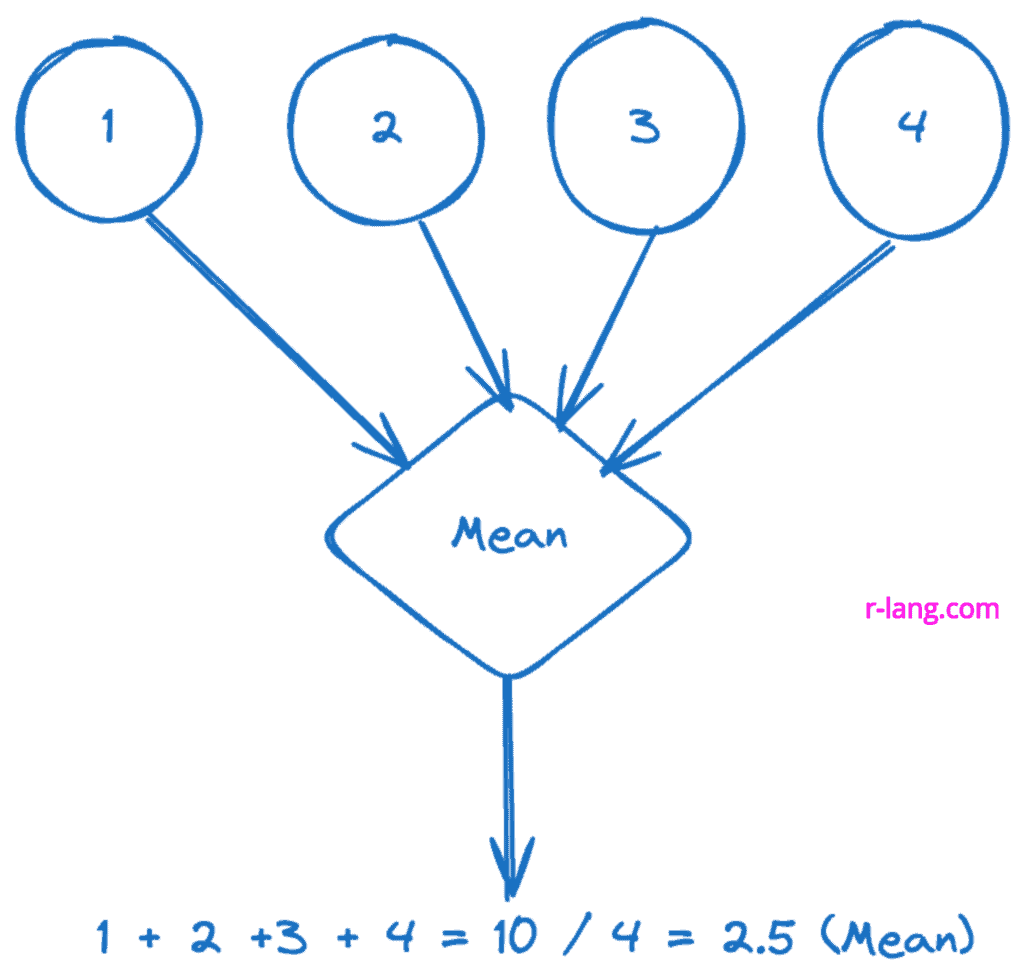
Mean means the arithmetic average of a number in mathematics. An average is the sum of the total numbers divided by the count of numbers.
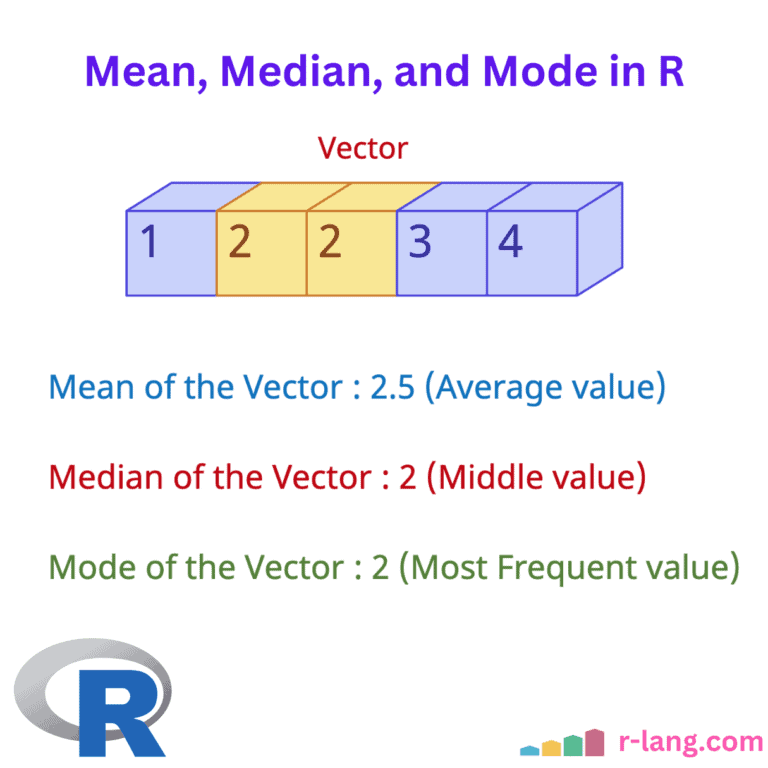
The above figure shows the mean of individual numbers, which is 2.5.
Vector
To calculate the arithmetic mean of a vector, use the mean() function.
In the above figure, we calculated the mean of the vector containing seven elements.
vec <- c(11, 21, 19, 18, 51, 51, 71)
# Calculating average using mean()
mean(vec)
# [1] 34.57143Data frame column
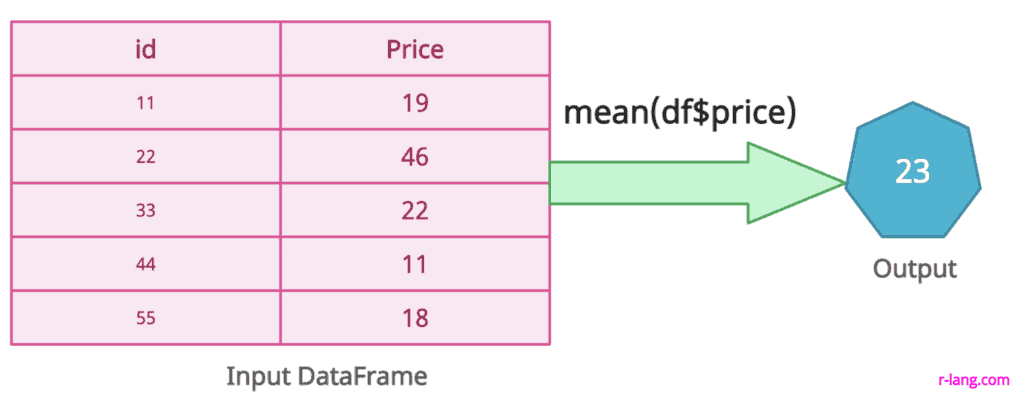
You can calculate the mean of a data frame column using the “mean(df$column)” expression.
The above figure returns the mean of DataFrame’s price column.
df <- data.frame(
id = c(11, 22, 33, 44, 55),
price = c(19, 46, 21, 11, 18)
)
# Calculate mean of DataFrame column
mean_of_col <- mean(df$price)
mean_of_col
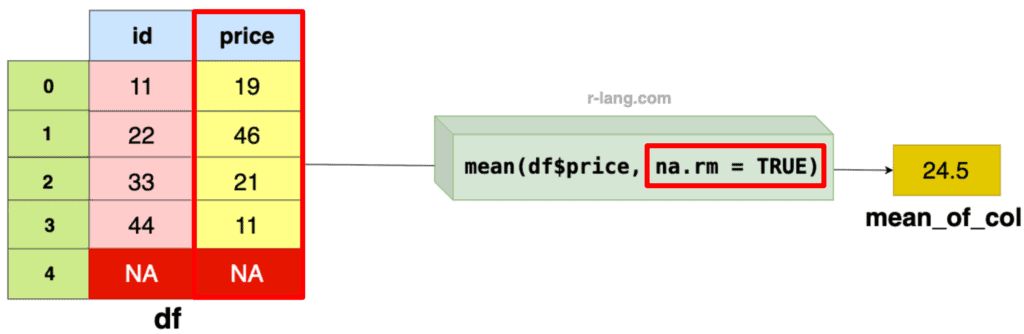
# [1] 23Excluding NA values
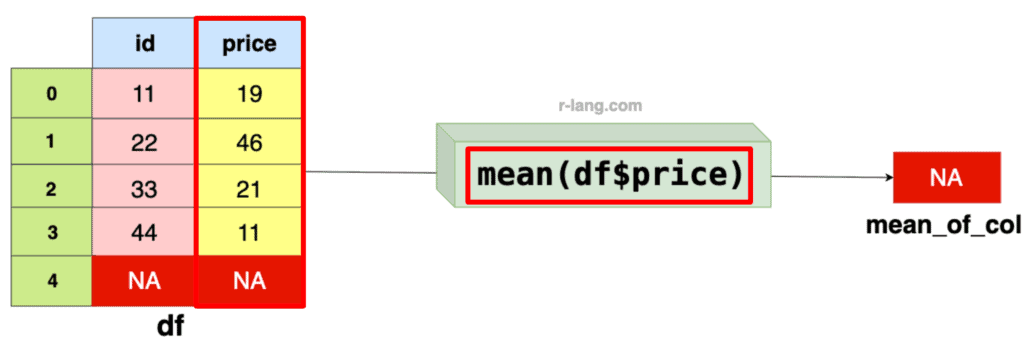
If your data frame contains NA values, it does not exclude them by default and returns NA as an output.
This is a default principle of missing or unknown values that makes the mean undefined or not meaningful.
df <- data.frame(
id = c(11, 22, 33, 44, NA),
price = c(19, 46, 21, 11, NA)
)
# Calculate mean of DataFrame column
mean_of_col <- mean(df$price)
mean_of_col
# [1] NA
In the above figure, we passed the na.rm = TRUE to the mean() function to skip the NA value while calculating the mean of the remaining column values.
df <- data.frame(
id = c(1, 2, 3, 4, NA),
price = c(11, 22, 33, 44, NA)
)
# Calculate mean of DataFrame column
mean_of_col <- mean(df$price, na.rm = TRUE)
mean_of_col
# [1] 24.5
In the above code example, we calculated the mean value of the price column’s (11, 22, 33, 44) values, excluding the NA values.
Median
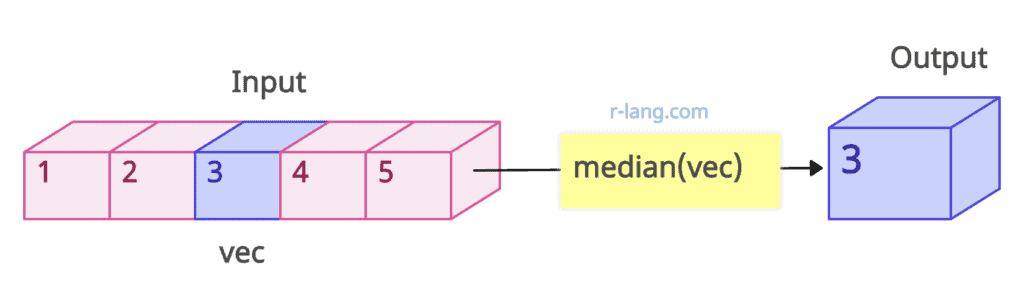
The median is the middle value of the ordered dataset from least to greatest.
Vector
You can use the built-in median() function to calculate the vector’s median. For an odd number of values in a vector, it will return the exact middle value. For an even number of values, it returns the average of the two medians.
vec <- 1:5
median(vec)
# [1] 3Let’s calculate for an even number of elements:
vec <- 1:6 median
(vec)
# [1] 3.5Data Frame
If you want to calculate the median of the data frame, you can do it by calculating a specific numeric column. For example, median(df$column).
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(1, 2, 3),
col2 = c(4, 5, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, 9)
)
# Calculate median of col1
median(df$col1)
# [1] 2
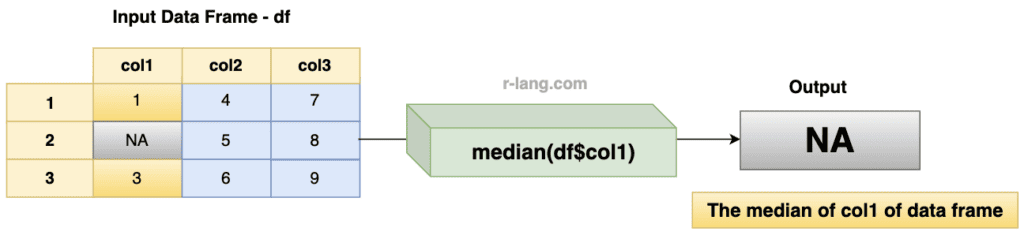
Handling NA values
If your data frame contains NA values, it will return NA as an output.
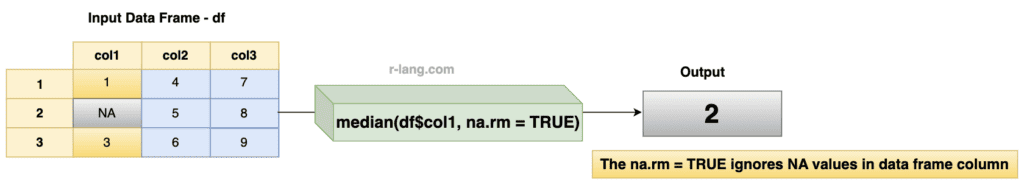
The above figure shows that we have a missing value, NA, as an output.
However, we can ignore the NA values in the dataset by using the na.rm = TRUE argument.
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(1, NA, 3),
col2 = c(4, 5, 6),
col3 = c(7, 8, 9)
)
# Calculate median of col1
median(df$col1, na.rm = TRUE)
# [1] 2Mode
The mode is the value that appears most frequently in your dataset. A datset can have unimode (1 mode), bimodal (2 modes), or multimodes. Using mode, you can identify the most common category or value in the dataset.
There is no built-in function in R that you can use to calculate the mode.
However, there are two different ways:
- Using the DescTools package’s Mode() function
- Creating a custom function
Method 1: DescTools package’s Mode()
Install and load the DescTools package:
install.packages("DescTools")
library(DescTools)
Mode of a numeric vector
library(DescTools)
numeric_vector <- c(11, 21, 19, 19, 12)
cat("The mode of numeric vector:", Mode(numeric_vector), "\n")
# The mode of numeric vector: 19
Mode of a character vector
library(DescTools)
character_vector <- c("k", "l", "b", "k")
cat("The mode of character vector:", Mode(character_vector), "\n")
# The mode of character vector: k
Method 2: Creating a custom function
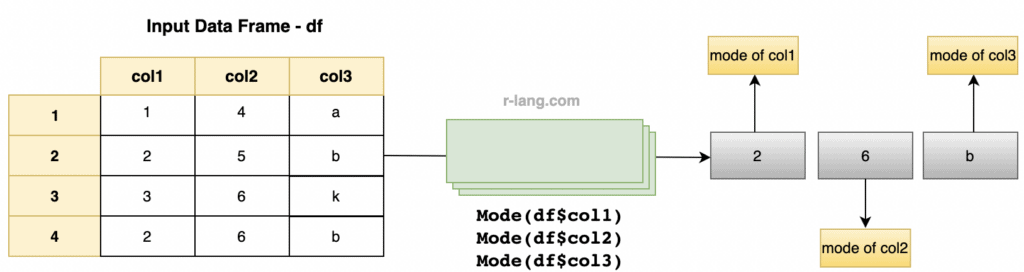
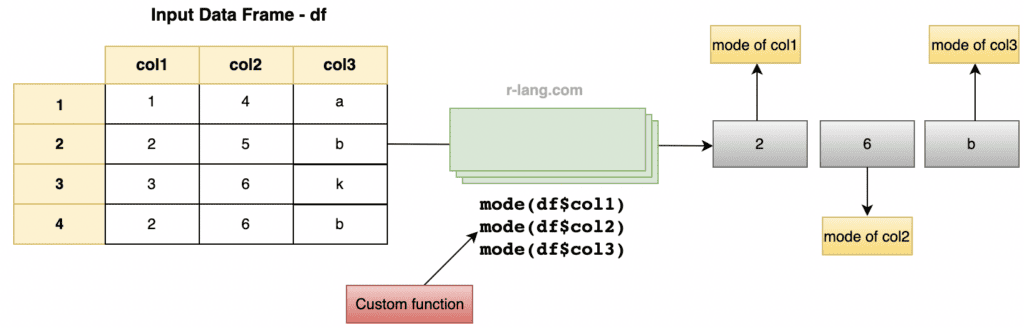
Let’s create a custom function to calculate the mode for data frame columns or a dataset.
mode <- function(x, na.rm = FALSE) {
if (na.rm) {
x <- x[!is.na(x)]
}
val <- unique(x)
return(val[which.max(tabulate(match(x, val)))])
}
df <- data.frame(
col1 = c(1, 2, 3, 2),
col2 = c(4, 5, 6, 6),
col3 = c("a", "b", "k", "b")
)
cat("The mode of col1 column:", mode(df$col1), "\n")
cat("The mode of col2 column:", mode(df$col2), "\n")
cat("The mode of col3 column:", mode(df$col3), "\n")
# The mode of col1 column: 2
# The mode of col2 column: 6
# The mode of col3 column: b
That’s it!

Krunal Lathiya is a seasoned Computer Science expert with over eight years in the tech industry. He boasts deep knowledge in Data Science and Machine Learning. Versed in Python, JavaScript, PHP, R, and Golang. Skilled in frameworks like Angular and React and platforms such as Node.js. His expertise spans both front-end and back-end development. His proficiency in the Python language stands as a testament to his versatility and commitment to the craft.