Dollar Sign ($ Operator) in R
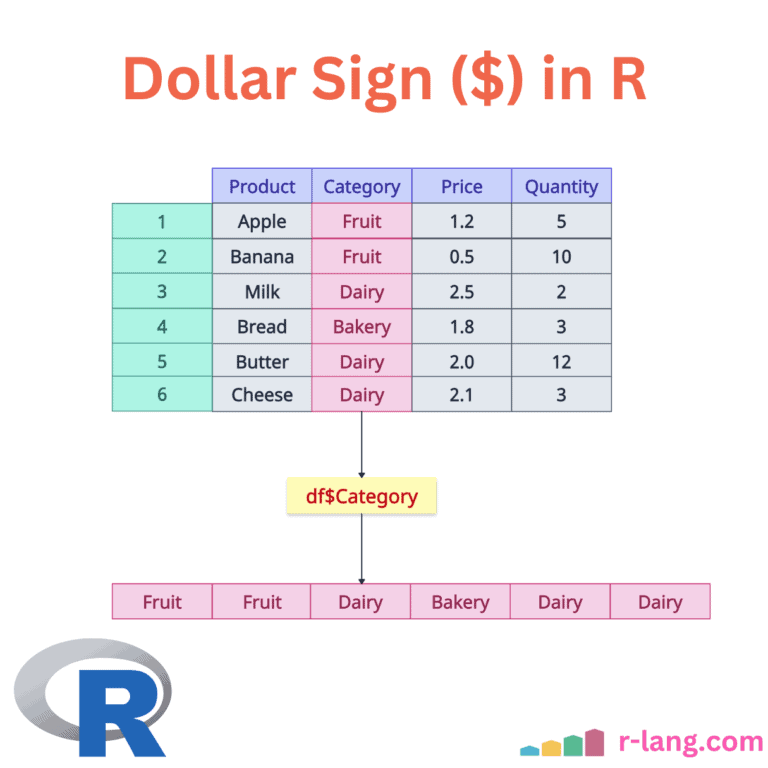
In R, you can use the dollar sign ($ operator) to access elements (columns) of a list or a data frame by their name. It also works with your environment. For example, it can fetch you the current environment variables. With its help, you can add, modify, or delete variables from the list and data … Read more